Deciding where to pursue medicine is possibly one of the most significant choices for Indian students. Besides fees and acceptance, the length of the course matters a lot. A lot of candidates, it seems, find themselves stranded in a predicament where they are comparing MBBS in India with MBBS in Georgia and want to know which is shorter, and why the difference exists.
Let’s break it down clearly.
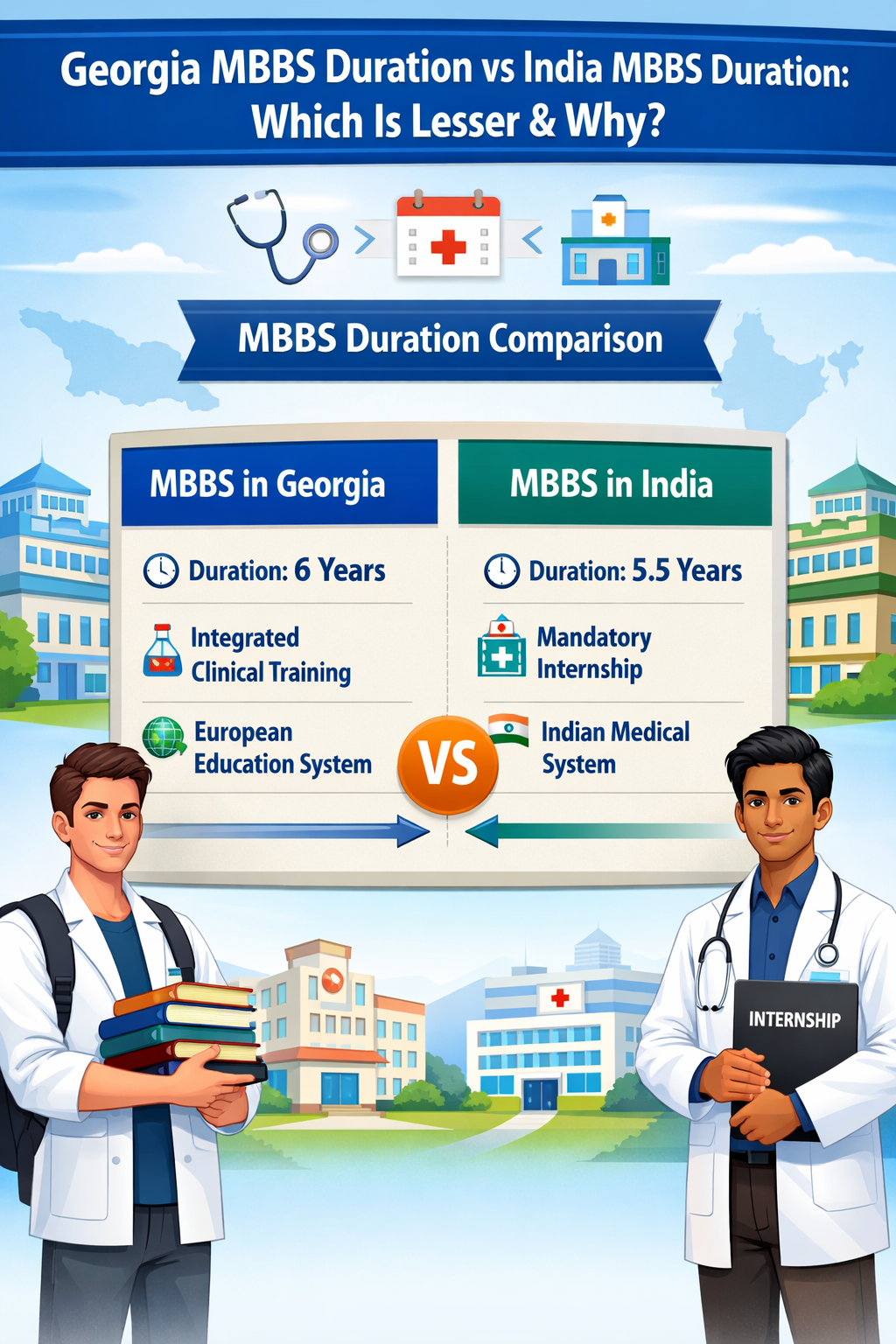
MBBS Duration in India
MBBS Duration in India:
5.5 years total
This includes:
- 4 ½ year academic education (theoretical and practical training combined)
- 1 year compulsory rotating internship
The internship is conducted at hospitals attached to the medical college, and it is mandatory as per the rules of the National Medical Commission (NMC). This internship is a mandatory requirement for graduation; without it students are not eligible for full registration as doctors practicing medicine in India.
MBBS Duration in Georgia
The MBBS duration in Georgia is as follows:
6 years total
This includes:
- 5 years of university-based training in academic medicine
- 1 year of clinical internship or an approved practice experience
So, technically speaking, Georgia’s program is 6 years, a little longer than India’s 5.5 years.
Which Is Shorter?
On paper:
- India MBBS → 5.5 years
- Georgia MBBS → 6 years
So India’s MBBS is 6 months shorter.
The disparity is a numbers game, but also a matter of educational structure.
Why MBBS in Georgia 6 Years?
The extended duration of MBBS in Georgia is primarily on account of its European-style medical curriculum. Georgian colleges and universities implement curricula meeting international standards that are recognized in the World Directory of Medical Schools (WDOMS).
Here’s why it takes 6 years:
- Integrated Clinical Exposure
You start your clinical training very early, and this is integrated throughout the entire course, rather than being just tacked on to the end of it. - European Credit Transfer System (ECTS)
Georgia uses the European model of education, which moves medical subjects throughout a fixed period. - Global Curriculum Standards
The programs are intended to be compliant with standards recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) for medical education.
That gives you a slightly longer, but conceptually global-alignment-oriented program.
Internship Difference: India vs Georgia
|
Aspect |
India |
Georgia |
|
Internship |
1 year compulsory in India |
Clinical training is included in the final year |
|
Structure |
Rotational hospital internship |
Integrated clinical practice |
|
Recognition |
Required by NMC |
Recognized if the university meets global norms |
Indian students who have completed MBBS from Georgia need to follow NMC guidelines after coming back, like you may have to do an internship or screening/licensing exams as and when existing regulations.
Does Duration Affect Degree Validity?
No. The duration of the course does not matter for the validity of the degree. What matters is:
- University recognition under NMC regulations
- Listing in WDOMS
- Curriculum being in line with the WHO's international standard of medical education
If those conditions are fulfilled, the degree is good for licensing exams.
Significance of NEET for Indian Students
Whether short-term or long-term, Indian students have to clear NEET UG in order to study MBBS abroad. As per NMC regulations, the NEET is a must for those keen to practice medicine in India after having studied abroad.
Academic Intensity Comparison
Most of the students are under the impression that the MBBS in Georgia's duration looks longer as compared to other universities, but it's not about how long you study; it's about what you study. In India, however, subjects are squeezed into fewer years, and semesters have a shorter duration.
Georgia’s system provides:
- Step-by-step subject progression
- Early patient interaction
- Strong practical orientation
That often leads to a more orderly classroom despite that extra half-year.
Final Verdict
|
Factor |
India MBBS |
MBBS in Georgia |
|
Duration |
5.5 years |
6 years |
|
System |
Indian medical curriculum |
European-style curriculum |
|
Clinical Training |
Mainly in the internship year |
Spread across the course |
|
Global Alignment |
National focus |
International standards |
The right one for Indian students is based on career aspirations, financial situation and future plans — not just the duration of courses.